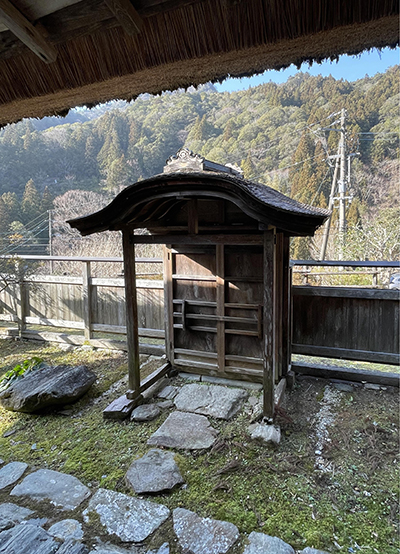
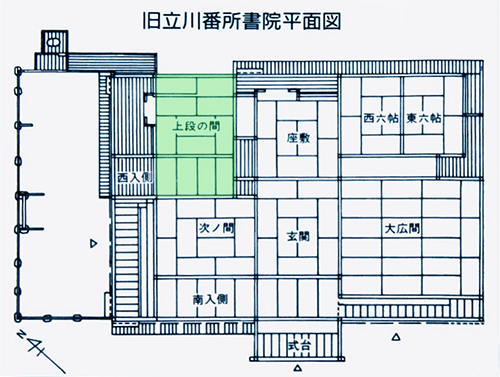
いちばん上の写真はこの番所で掲示されていたパネル写真の転載。いまの高知県と愛媛県の県境に位置する立川ですが、高地なのでこんなに積雪する気候条件なのだという。調べてみると1月の最低気温は0°。こういう気候環境では北海道と大差のない建築仕様が求められると思うけれど、建築当時も今も建築専門家は高知市や大豊などの人口集積地の各都市に拠点を持っているケースが圧倒的だろうから、気候条件は温暖〜蒸暑地の平地の感覚でしか対応しなかったことだろう。
事実、積雪寒冷に対応するような建築仕様はもちろん考慮されず、外気に対して写真のように、障子の「紙」だけで対応し主室の殿様も厠にはいったん外に出てアクセスしていた。藩主という資金も権力もある存在の超高級住宅「陣屋」建築でも確かにやりようはなかった。
冷気との戦いということでは、全開放された「縁」のことがまずは考えられる。庭や周辺の山々という「見え」環境条件を最優先しているとはいえ、雨戸のような戸板程度は対応があっただろうが、それでも障子紙1枚+戸板での「ウチ・ソト」分離仕切りとならざるを得ない。言うまでもなく熱環境的には意味は薄い。
この建物とそう時代が違わない明治初年の北海道開拓使が計画した官営建築では、雨戸の部位にさっそく「ガラス窓」が装置された。開拓使は「ガラス邸」とこの建築を名付けて寒冷地住宅としての「モデルハウス」機能を持たせることを企画し、事実、見学参観者が大量に押しかけて「建築材料として気密性に優れたガラスを使う」実例を学んだ。
当時は輸入専門だったガラス建材は高価だったけれど、北海道では「気密建材」のメリットが評価されて、どんな奥地の貧しい開拓者の家でも採用されたという。当時ガラス輸入を手掛けていた有力企業にその歴史事情をヒアリングしたことがあるが、北海道マーケットがガラス建材市場に占めていた割合は当時50%を超えていたという。
話を立川の番所に戻すと、こういう環境では血圧上昇は避けられなかっただろう。健康面ではかなりハードな環境。参勤交代のようなセレモニーであれば対幕府の外交を通して移動する季節を調整するなども可能だっただろうけれど、幕末の政治動乱期には京都情勢などでいつ何時にも、藩主は移動する必要があっただろう。
こういう環境の中を明治維新動乱の土佐の主要人物、藩主・山内容堂などは実際に移動していたと考えると、維新の激動期の隠れた実相が見えてくるようで興味深い。そもそも幕末の政局要件には南下侵略するロシアから、どう国土を、とくに寒冷地北海道を守り抜くかということが大きなテーマだったのだ。寒冷地住宅についてのその後の政治指導者・黒田清隆の積極姿勢などは、こういう土佐の政治指導者の日常的体験なども多少は関わっていたかも知れないと空想させられる。
English version⬇
Snow and cold in the highlands of Shikoku.
The Tosa domain lord Yodo Yamauchi repeatedly moved to Kyoto, the center of political affairs, in such snowy and cold weather. Did he influence the concept of defense of Hokkaido, a cold region? …
The top photo is a reproduction of a panel photo displayed at the guardhouse. Tachikawa is located on the border between Kochi and Ehime prefectures. The lowest temperature in January is 0°C. In this kind of climatic environment, architectural specifications that are not much different from those of Hokkaido would be required. However, architectural specialists at the time of construction and even today would have been overwhelmingly based in cities with high population density, such as Kochi City and Otoyo, and would have dealt with climatic conditions only in the sense of warm to hot humid flatland areas.
In fact, the building specifications were not designed to cope with snow and cold, and as shown in the photo, only the “paper” of the shoji screens was used to deal with the outside air, and even the lord of the main room had to go outside to access the restroom. This was certainly not possible even for the construction of the “Jinya,” a super-luxury residence for the feudal lord, who had both money and power.
In terms of fighting against the cold air, we can first think of the “rim” that was fully opened to the public. Even though the “visible” environmental conditions of the garden and the surrounding mountains were given top priority, a door panel like a storm door could have been used, but even so, a single sheet of shoji paper plus a door panel was the only way to separate the “home from the garden. Needless to say, this is of little significance in terms of the thermal environment.
In a government-run building planned by the Hokkaido Kaitakushi (Hokkaido Development Office) in the early Meiji period (1868-1912), which is not so different from this building, a “glass window” was immediately installed as a part of a storm door. The Kaitakushi planned to name the building the “Glass House” to serve as a “model house” for cold-weather housing, and in fact, many visitors came to see the building and learn about the use of glass as a building material with excellent airtightness.
At the time, glass building materials, which were imported exclusively, were expensive, but in Hokkaido, the advantages of “airtight building materials” were highly regarded, and they were used in the homes of poor pioneers in even the remotest parts of the island. I once interviewed a leading glass importer who told me that the Hokkaido market accounted for more than 50% of the glass building materials market at the time.
Returning to the Tachikawa watchtower, an increase in blood pressure would have been inevitable in such an environment. A very hard environment from a health standpoint. If it had been a ceremonial visit, it would have been possible to adjust the season of travel through diplomacy with the shogunate, but during the period of political upheaval at the end of the Edo period, the feudal lord would have had to travel at any time of the year, depending on the situation in Kyoto and other factors.
It is interesting to consider that the major figures in Tosa during the Meiji Restoration, such as the feudal lord Yodo Yamauchi, actually moved around in this environment, revealing the hidden reality of the turbulent period of the Meiji Restoration. The main theme of the political situation at the end of the Tokugawa Shogunate was how to protect the country, especially the cold region of Hokkaido, from the invading Russians to the south. It makes us wonder if the aggressive stance of Kiyotaka Kuroda, a later political leader, regarding cold-weather housing may have had something to do with the daily experiences of such a Tosa political leader.
Posted on 4月 23rd, 2023 by 三木 奎吾
Filed under: 住宅性能・設備, 歴史探訪 | No Comments »