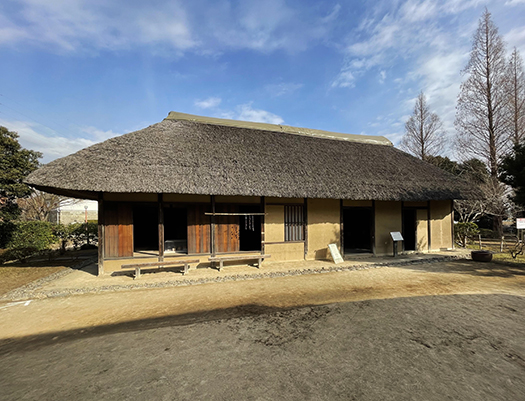
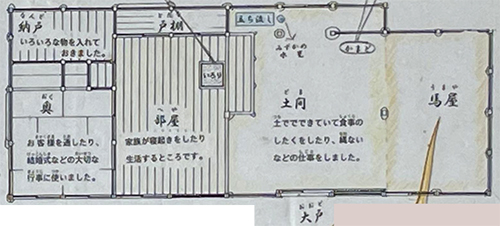
最近の東京・関東出張では東京ビッグサイトを訪問することがメッチャ多い。わたしが関係する住宅などのイベントの常打ち会場であることが多いワケなのですが、それ以外の興味領域でも使用される割合が多く実感的にはほぼ毎回顔を出している状況です。正面外観は毎度、こんな顔で迎えてくれる。
なんとなく馴染みになってくる感覚があってキライではない。
東京湾の埋め立て地に立地していて、新橋からゆりかもめで大体30分程度。広大な敷地と室内空間面積の「展示場施設」としての利便性は高い。いま考えれば合理性もあるけれど、沿革を見ると以下。
「延床面積は約25ヘクタール総展示面積は約9.5ヘクタール。 建築総工費は1985億円。 東京都が1995年に世界都市博覧会(都市博)の会場として建設したが、青島幸男都知事の判断で都市博が中止になったため、中央区晴海(はるみ)にあった東京国際見本市会場を移転する形で開業した。」
で、見ているうちに、形態について深層心理みたいなことを想起するようになって、日本の宗教建築の屋根の張り出し、せり上がりがこの三角プロポーションとアナロジーさせられるようになって来た。4つ足の立柱と三角錐とのバランスが腑に落ちるようになってくる。下の写真は鹿島神宮桜門。
設計は(株)佐藤総合計画という現在所員数324名という組織設計事務所。
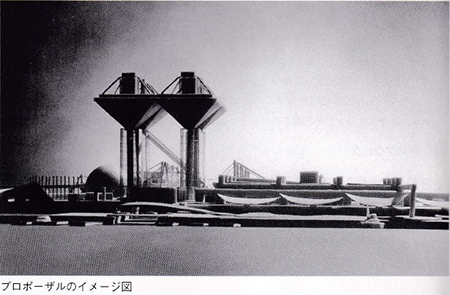
設計当初のプロポーザル案はこちらのような形態で、どうも「天空の城ラピュタ」がイメージとしてあったのだそうです。東京都のプロポーザル案件だったので、審査員には「多様な見方」を反映する意味で建築専門家以外のひとも多いことを見越して「わかりやすい」点を重視したモノでしょう。
ただその後、実施段階になってドンドン脚部が膨らみ、ズングリムックリ型になっていったとのこと。そして当初のイメージとは変容して日本的宗教建築のプロポーションに近づいていったのか。
埋め立て地域なのでとくに外観意匠にはチタン素材などの錆びない建材が多用されている。形態がどんどん宗教建築に近づいていったのに、そう感じさせずにモダンデザイン風に受け取ってきていたのには、そういった素材感からの「パッと」見の要素が大きいでしょうね。
ちょうどガウディの宗教建築・サグラダファミリアの設計趣旨展示会も東京近代美術館で開かれていて、建築デザインの趣旨説明をいろいろな側面からひもといていたので、それとの対比での「日本建築」としての見方をこのビッグサイト外観に当てはめてみた次第です。
まぁ、建築は出来上がってしまえばだれからも公平に端的に、見られる存在になるので、思った感じたことは、自由に論じあうべきものだと思います。わたしはこういう建物、悪くないと思う。
English version⬇
Tokyo Big Sight and Religious Architectural Design
Gaudi created the Sagrada Familia from the historical design of Christian and Islamic architecture in a unique way. What is the sense of form that is common to modern Japan? ……
On my recent business trips to Tokyo and the Kanto region, I have been visiting Tokyo Big Sight quite often. The site is often a regular venue for housing and other events that I am involved with, but it is also used for many other areas of interest as well, so I feel that I am visiting the site almost every time I am there. The front exterior greets us with a face like this every time.
It is not bad, as it has a sense of familiarity.
Located on a reclaimed land in Tokyo Bay, it takes about 30 minutes from Shimbashi by Yurikamome. It is highly convenient as an “exhibition facility” with its vast site and indoor space. The history of the building is as follows.
The total floor space is approximately 25 hectares, and the total exhibition area is approximately 9.5 hectares. The total construction cost was 198.5 billion yen. It was built by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government in 1995 as the venue for the World Urban Exposition (Urban Expo), but when Governor Yukio Aoshima decided to cancel the Expo, the Tokyo International Trade Fair Center was relocated to Harumi, Chuo-ku, and opened.
As I looked at the building, I began to think about the deep psychology of form, and began to make analogies between the triangular proportions of the overhanging and overhanging roofs of Japanese religious buildings and the balance between the four-legged standing columns and the triangular pyramid. The photo below shows the Kashima Jingu Shrine.
The design is by Sato Sogo Keikaku, an organizational design firm with 324 members.
The initial design proposal was based on the image of “Laputa: Castle in the Sky. Since this was a Tokyo Metropolitan Government proposal project, the jury members included many non-architectural specialists in order to reflect “diverse views,” and the emphasis was probably placed on “easy-to-understand” points.
However, the legs of the building swelled and became larger and larger as the project progressed to the implementation stage. The proportions of the building were transformed from the original image and became closer to the proportions of a temple building.
Because this is a reclaimed area, titanium and other rustproof construction materials were used extensively, especially for the exterior design. The fact that the form of the building was getting closer and closer to religious architecture, yet it was received in the style of modern design without giving that impression, must have been largely due to the “poof” factor from the texture of such materials.
The exhibition of the purpose of Gaudi’s religious building, Sagrada Familia, was also being held at the Museum of Modern Art, Tokyo, and I was looking into the design of the building from various aspects, so I tried to apply my view of “Japanese architecture” to the exterior of the Big Sight in comparison with the exhibition.
Well, once the architecture is completed, it will be seen fairly and straightforwardly by everyone, so I think we should freely discuss what we think and feel about it. I think this kind of building is not bad.
Posted on 7月 25th, 2023 by 三木 奎吾
Filed under: 「都市の快適」研究, 住宅マーケティング | No Comments »